Cursos relacionados
Ver Todos os CursosIntermediário
RAG Theory Essentials
A comprehensive, theory-focused course on the core concepts, architectures, and evaluation strategies behind Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. Designed for learners seeking a deep understanding of why RAG exists, how retrieval and generation are integrated, and how to evaluate and improve RAG pipelines.
Avançado
Transformers Theory Essentials
A comprehensive, code-free exploration of transformer-based language models, focusing on their architecture, text generation mechanics, and the theoretical principles underlying their behavior.
Intermediário
Knowledge Graphs and Embeddings
An intermediate, theory-first course introducing the foundations of knowledge graphs, their embedding models, and reasoning techniques, with hands-on Python demos using numpy and networkx.
GraphRAG for Connecting the Dots Beyond Vector Search
Unlocking Complex Reasoning in AI with Knowledge Graphs
Imagine asking a powerful AI assistant a complex business question like "How does the supply chain shortage in Component A affect the delay of Project B?".
Standard AI search methods often fail here. They might find documents about "Component A" and separate documents about "Project B", but they miss the hidden relationship between them because those documents don't share similar keywords.
This is where GraphRAG enters the picture. It moves beyond simply finding relevant text to understanding the structure and relationships within the data.
The Limitation of Vectors and The Detective Problem
To understand why GraphRAG is necessary, imagine a detective trying to solve a crime.
- Standard search (vector RAG) is like a keyword search through a filing cabinet. If the detective searches for "suspect", they get every file containing that word;
- GraphRAG is like the detective's pinboard on the wall. It connects photos with red string, showing that "Person A called Person B, who owns the Car C found at the Crime Scene".
Traditional methods are excellent at measuring similarity (how close two sentences are in meaning), but they struggle with complex reasoning (multi-hop retrieval). If the answer to your question is split across three different documents, a standard system will likely miss the connection.
Core Concept and Knowledge Graphs
At the heart of GraphRAG lies the knowledge graph. Unlike a standard database (rows and columns) or a vector database (lists of numbers), a graph database stores data as a network.
It consists of two main elements:
- Nodes which represent the entities (people, places, concepts, companies);
- Edges which represent the relationships between them.
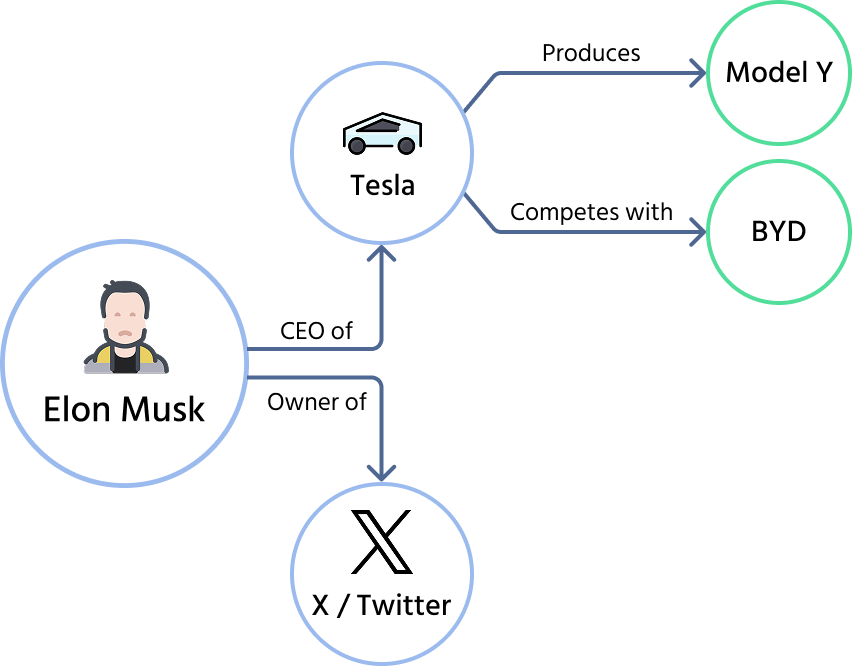
In the diagram above, the system doesn't just know the text "Elon Musk". It understands his relationship to specific companies and products.
How GraphRAG Works
GraphRAG combines the power of Large Language Models (LLMs) with Knowledge Graphs. The process generally involves two phases: indexing (building the graph) and querying (using it).
Phase 1 Graph Extraction
When you feed documents into a GraphRAG system, an LLM reads the text and automatically extracts entities and relationships.
Input text: "Apple released the Vision Pro. Tim Cook announced the pricing."
LLM extraction:
- Entity:
Apple(Company); - Entity:
Vision Pro(Product); - Entity:
Tim Cook(Person); - Relationship:
Apple-> released ->Vision Pro; - Relationship:
Tim Cook-> works for ->Apple.
Phase 2 Community Summarization
One of the most powerful features of modern GraphRAG is community detection. The system groups closely related nodes into communities and generates summaries for them.
When a user asks a global question like "What are the major risks in our dataset?", the system doesn't need to read every document. It simply reads the pre-generated summaries of the relevant communities.
Comparison of Vector RAG vs GraphRAG
| Feature | Standard Vector RAG | GraphRAG |
|---|---|---|
| Data Representation | Numerical embeddings (Vectors) | Nodes and Edges (Network) |
| Best for... | Specific, factual lookups ("What is the price?") | Global questions & connecting dots ("How does X affect Y?") |
| Reasoning Type | Semantic Similarity | Structural / Multi-hop Reasoning |
| Setup Cost | Low (Fast to index) | High (LLM must read text to build graph) |
| Performance | Fast retrieval | Slower, but deeper analysis |
Real-World Use Cases
GraphRAG is particularly valuable in domains where the connection is more important than the content of a single document.
Financial Fraud Detection
Criminals often use complex networks of shell companies to hide money laundering.
- Vector search might find a document about "Company A";
- GraphRAG can detect that "Company A" shares a phone number with "Company B", which shares an address with "Person C", who is on a sanctions list. It traces the path of fraud.
Medical Research and Drug Discovery
Biological systems are networks.
- Vector search finds papers mentioning "Protein X";
- GraphRAG maps out that "Drug A" inhibits "Protein X", which regulates "Gene Y", potentially curing "Disease Z". It accelerates hypothesis generation.
Supply Chain Intelligence
Consider a scenario with a factory fire in Taiwan. GraphRAG instantly maps which suppliers use that factory, which products use those parts, and which customer contracts will be delayed as a result.
Is It Worth It?
If GraphRAG is so powerful, why doesn't everyone use it? The answer lies in cost and latency.
- Expensive indexing: Building a knowledge graph requires an LLM to process every sentence of your data to extract entities. This consumes significantly more tokens (and money) than simply creating vector embeddings;
- Complexity: managing a graph database (like Neo4j) is more complex than a vector database (like Pinecone or Milvus).
Cursos relacionados
Ver Todos os CursosIntermediário
RAG Theory Essentials
A comprehensive, theory-focused course on the core concepts, architectures, and evaluation strategies behind Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. Designed for learners seeking a deep understanding of why RAG exists, how retrieval and generation are integrated, and how to evaluate and improve RAG pipelines.
Avançado
Transformers Theory Essentials
A comprehensive, code-free exploration of transformer-based language models, focusing on their architecture, text generation mechanics, and the theoretical principles underlying their behavior.
Intermediário
Knowledge Graphs and Embeddings
An intermediate, theory-first course introducing the foundations of knowledge graphs, their embedding models, and reasoning techniques, with hands-on Python demos using numpy and networkx.
RAG for Bridging the Gap Between AI and Your Data
How to Teach AI to Use Your Private Data Without Hallucinations
by Arsenii Drobotenko
Data Scientist, Ml Engineer
Feb, 2026・10 min read

Best Ways To Use ChatGPT for Improving School Performance Without Cheating
Use ChatGPT for Best Performance
by Anastasiia Tsurkan
Backend Developer
Dec, 2023・3 min read

Explainable AI - Why It Matters and How It Works
From Confusion to Clarity: Making AI Decisions Transparent and Accountable
by Arsenii Drobotenko
Data Scientist, Ml Engineer
Jun, 2025・10 min read

Conteúdo deste artigo