Related courses
See All CoursesIntermediate
Git Essentials
Git is the most popular version control system used by millions of developers around the globe. Whether you're a seasoned developer or a beginner, this course will equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to efficiently manage your software projects, collaborate with others, and master the art of version control.
Beginner
Linux Basics
Learning Linux is valuable for many IT professions. For system administrators, DevOps engineers, and backend developers, it enables efficient server management, automation of software development and deployment, and the development and management of server-side applications. For network administrators, cybersecurity professionals, and data analysts, Linux knowledge helps effectively manage networks, ensure security, and analyze data.
Guide to Installing Docker on Windows and Mac
A beginner-friendly guide to getting Docker up and running on your computer.

Docker is a tool that helps create, run, and manage applications in a specialized environment.
Docker simplifies and speeds up the development and testing of applications. Instead of worrying about server setup or environment configurations, developers can work with containers, which provide a standardized environment for running applications.
In this article, we'll walk through how to install Docker on Windows and macOS and how to verify that Docker is installed properly.
Installing Docker on Windows
Open your web browser, go to the official Docker website, and click "Download for Windows" to start downloading the .exe file.
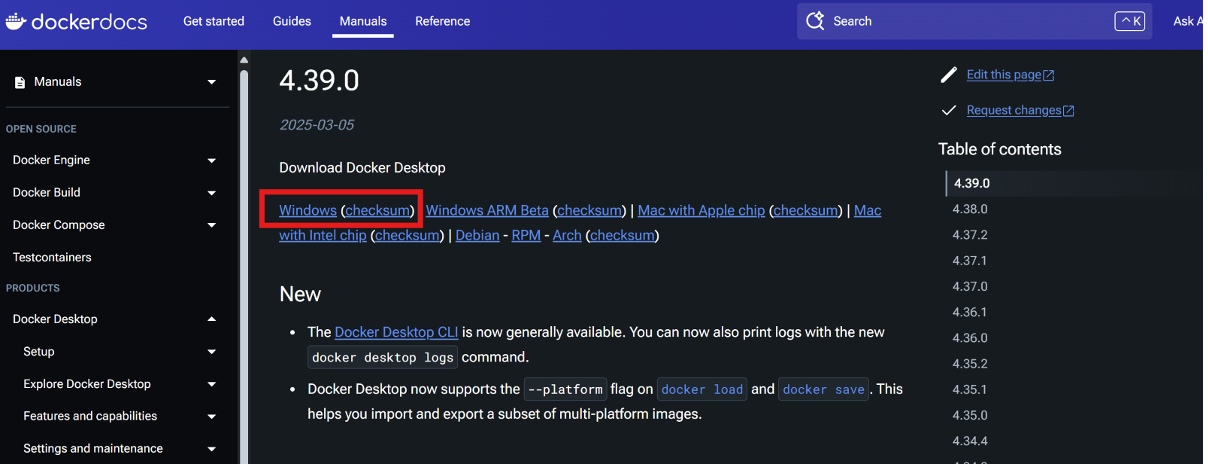
Run the Installer – Double-click the downloaded .exe file to launch the Docker Desktop Installer.
Select Installation Options –
-
Ensure “Use WSL 2 instead of Hyper-V” is checked (recommended);
-
If you do not have WSL 2 installed, Docker will prompt you to install it.

Click "Ok" – wait for Docker to install on your system.
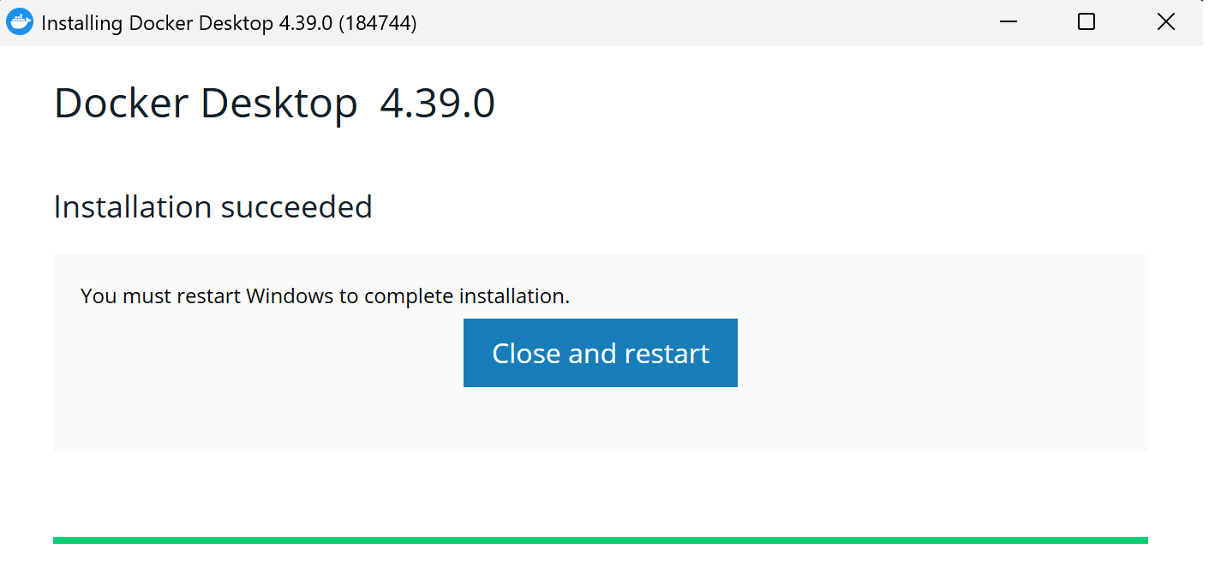
Once the installation is complete, click "Close and Restart" to apply changes.
Run Code from Your Browser - No Installation Required

Launch and Configure Docker on Windows
Open Docker Desktop from the Start Menu.
When prompted, sign in or create a Docker Hub account. Or you can just skip this step by clicking the "Skip" button in the top right corner.
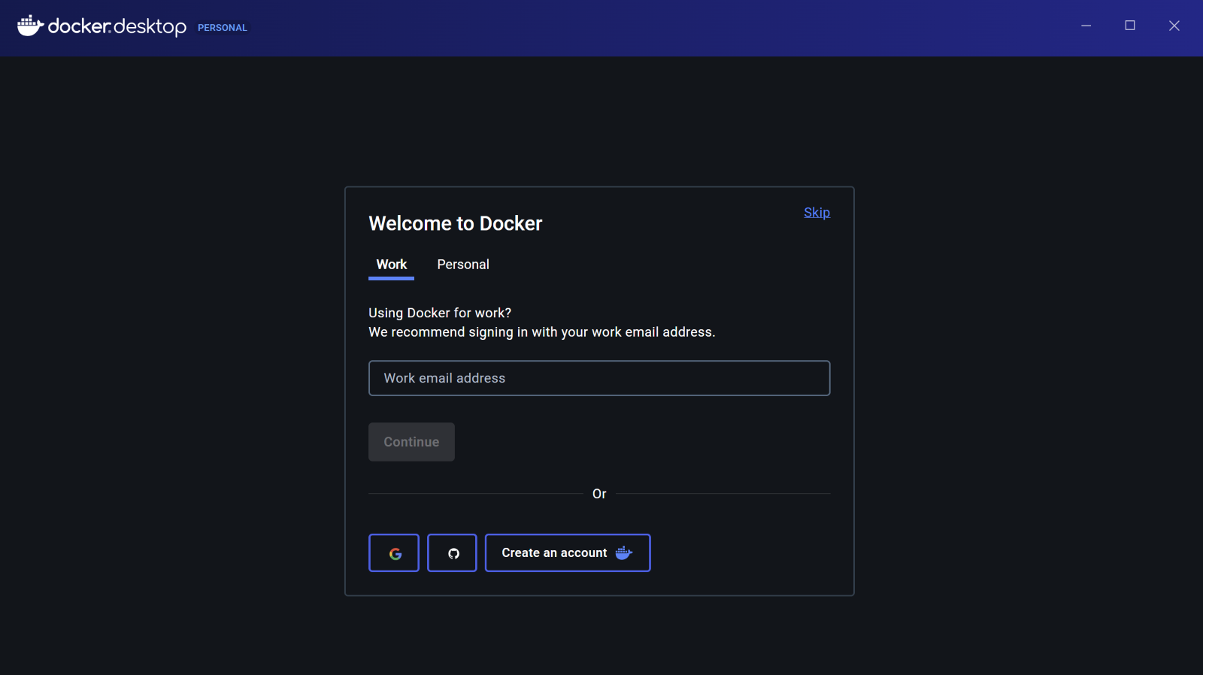
Once signed in, Docker will start running in the background.
Verify Docker Installation
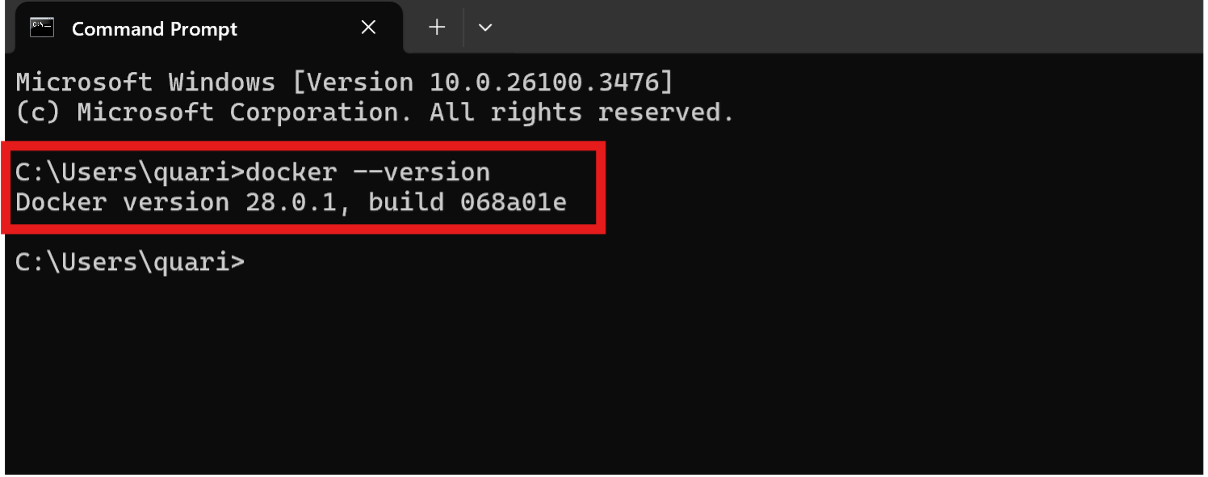
Open PowerShell or Command Prompt and type: docker --version. If installed correctly, you’ll see output like: Docker version 28.x.x .
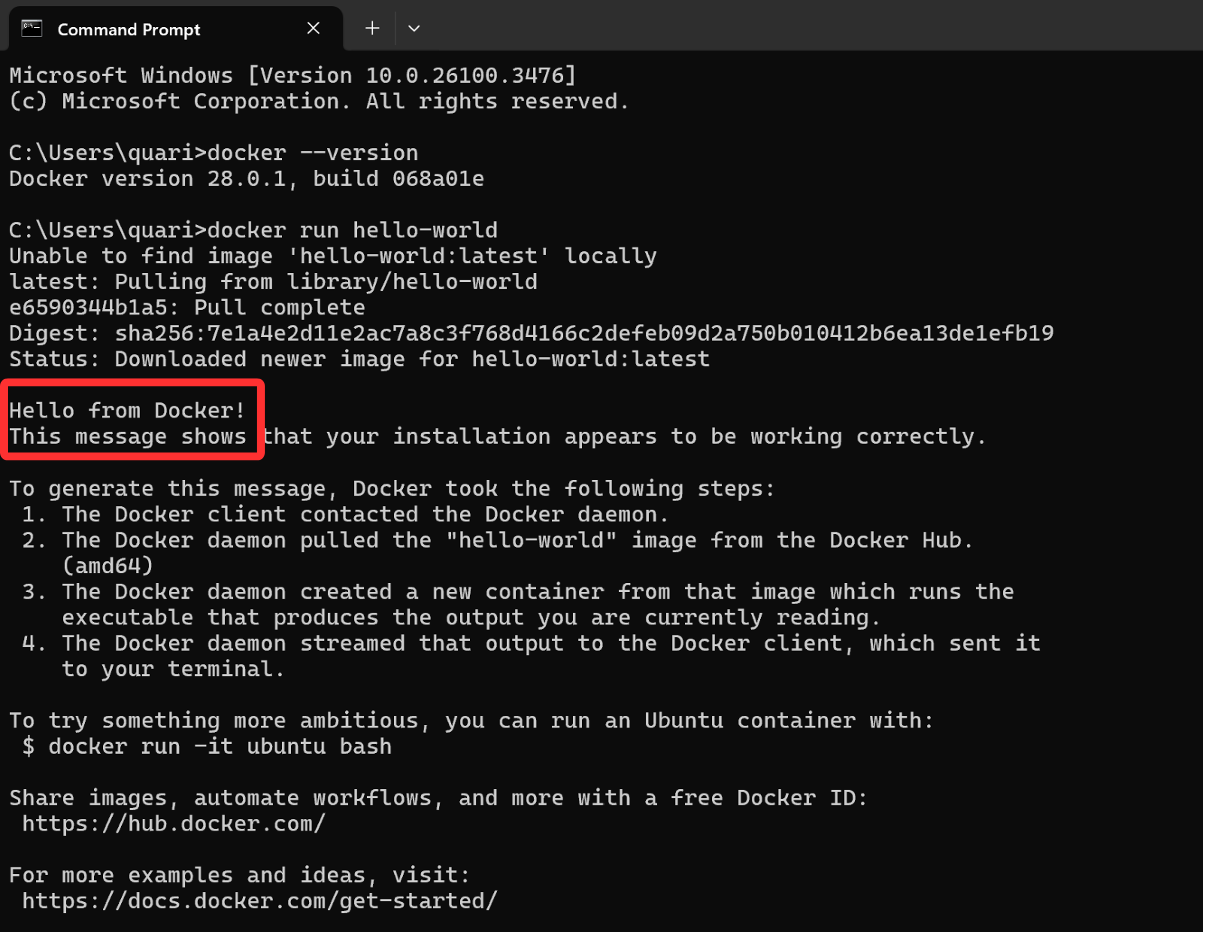
Run the Docker test container: docker run hello-world. If Docker is working correctly, you’ll see a message confirming that Docker is running: Hello from Docker!
Installing Docker on macOS
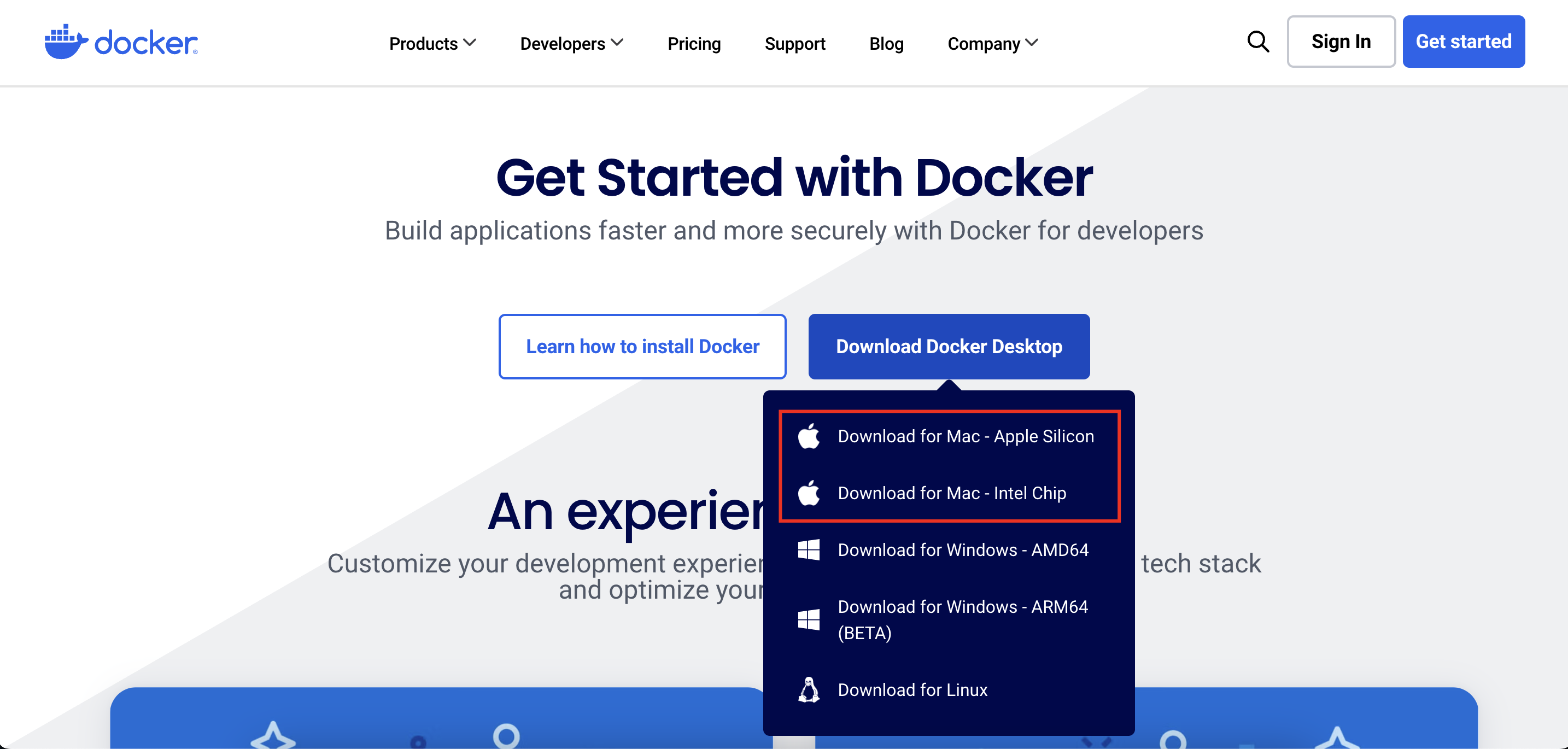
Open your web browser, go to the official Docker website Docker website, click "Download for Mac".
Wait for the .dmg file to download, and then find it in your Downloads folder.
Open the .dmg file – This will mount the Docker Desktop installation package. Drag and drop the Docker icon into the Applications folder.
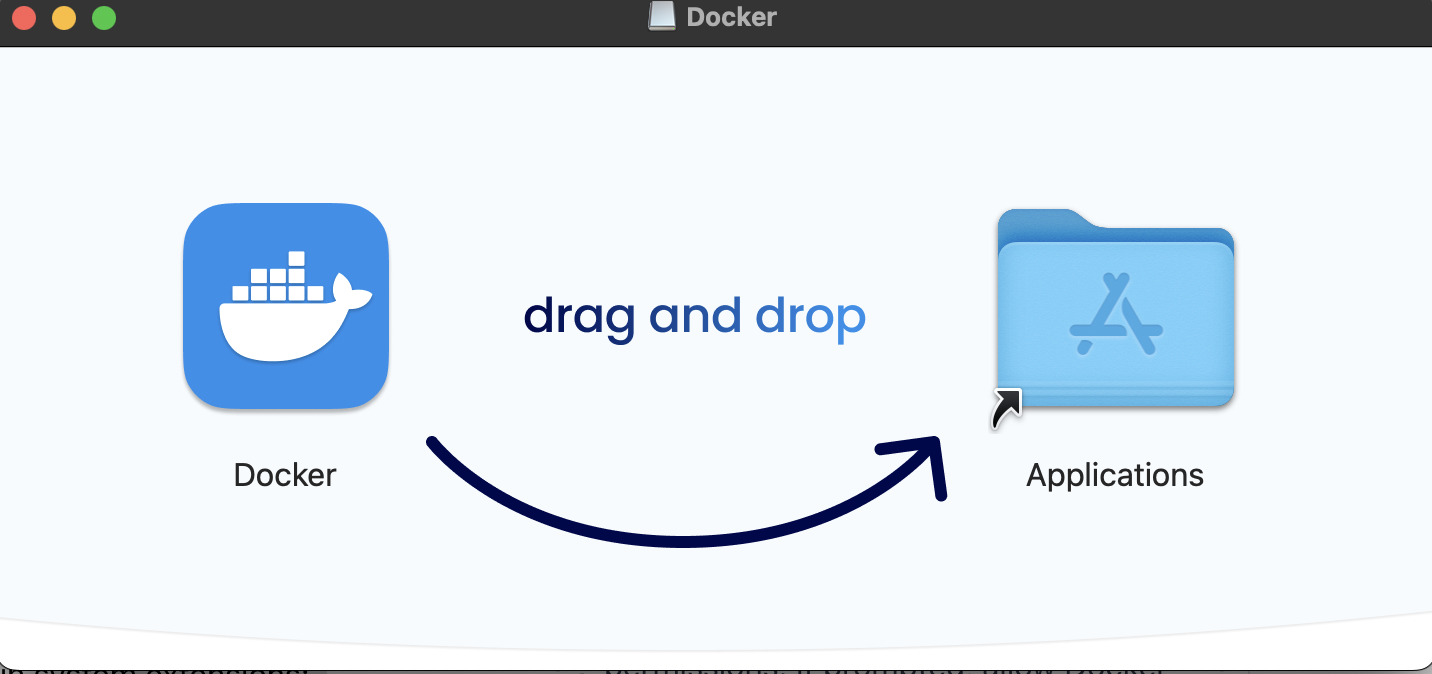
Open Docker from the Applications folder – the first time you launch it, macOS may prompt you to grant security permissions.
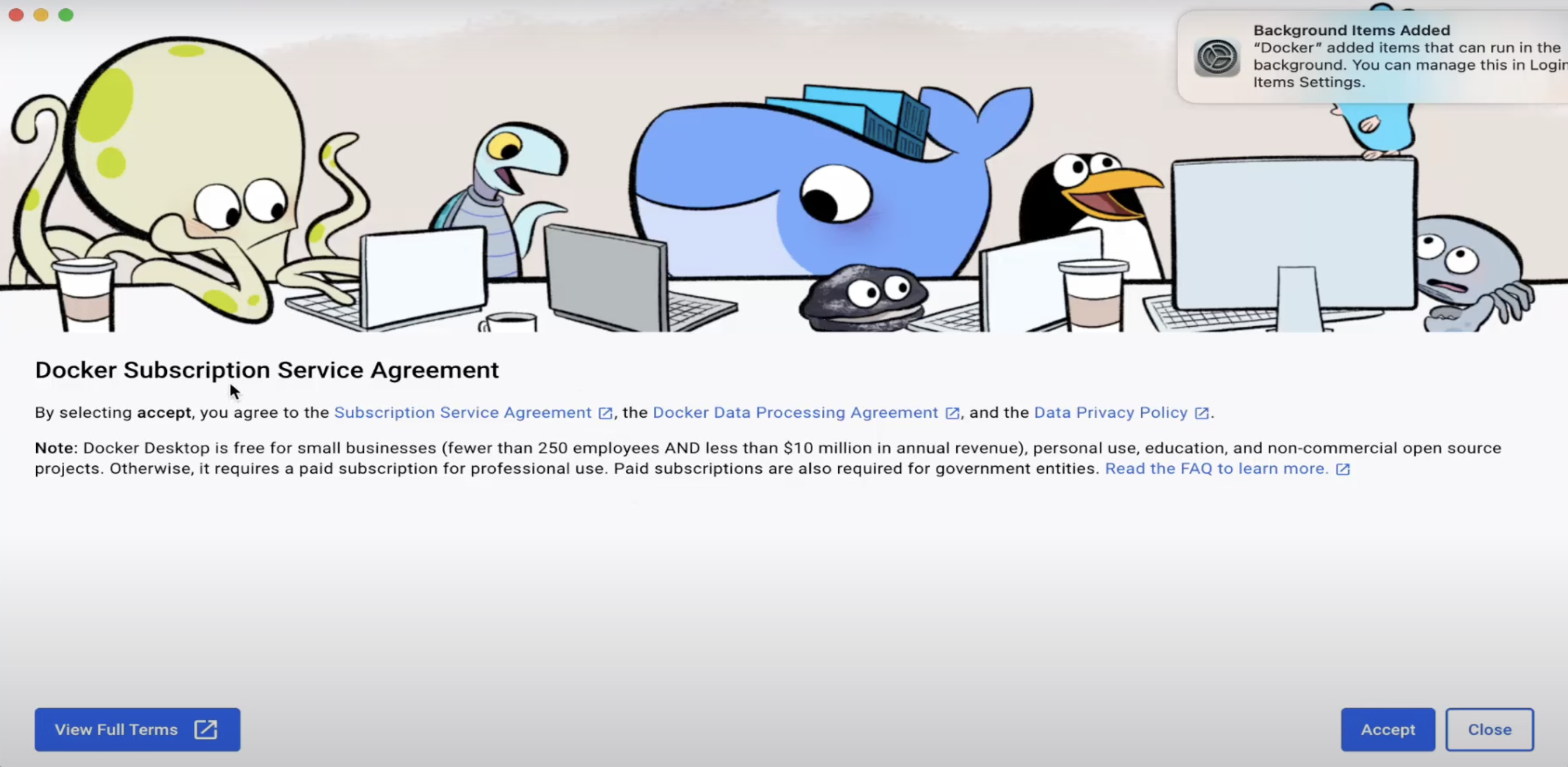
Accept the License Agreement – Click "Accept" and proceed.
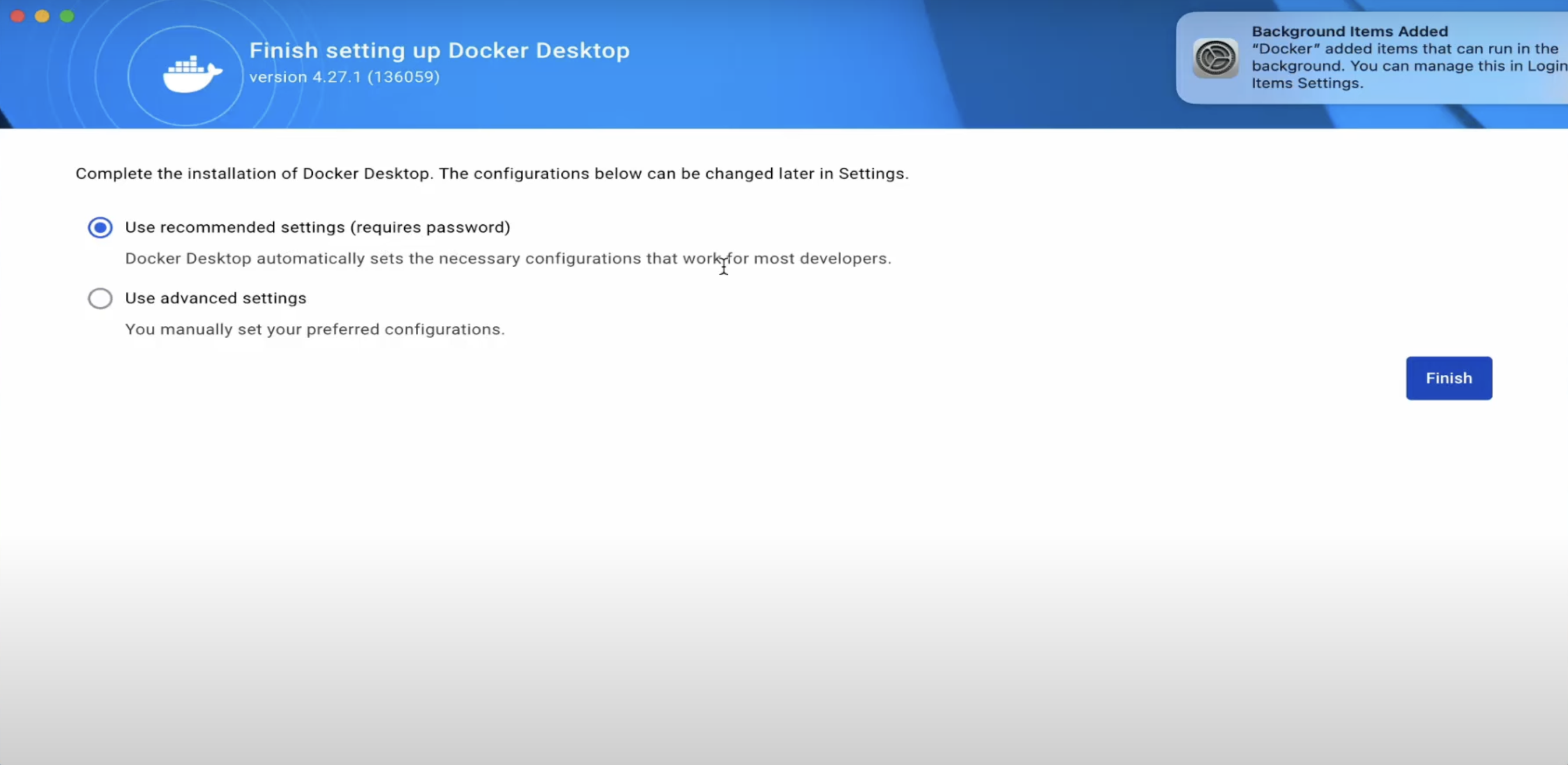
When prompted to complete the setup, choose Use recommended settings (requires your password). This option automatically applies the default configuration, which works well for most developers.
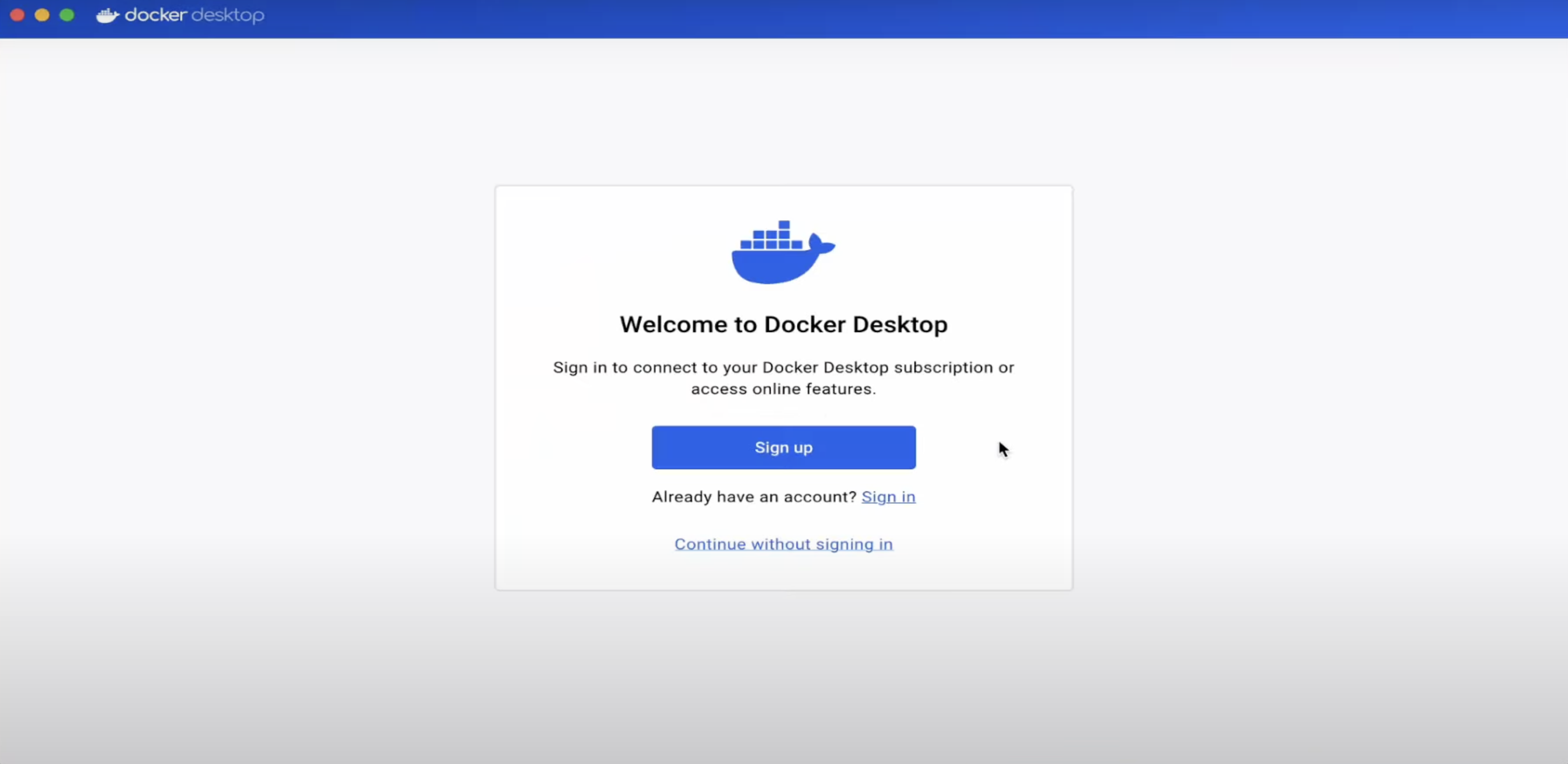
After the setup, Docker will prompt you to sign in or create an account. You can skip this step by clicking "Continue without signing in" at the bottom of the window.
Docker will start running in the background, and the Docker whale icon will appear in the top menu bar.
Start Learning Coding today and boost your Career Potential

Verify Docker Installation on macOS
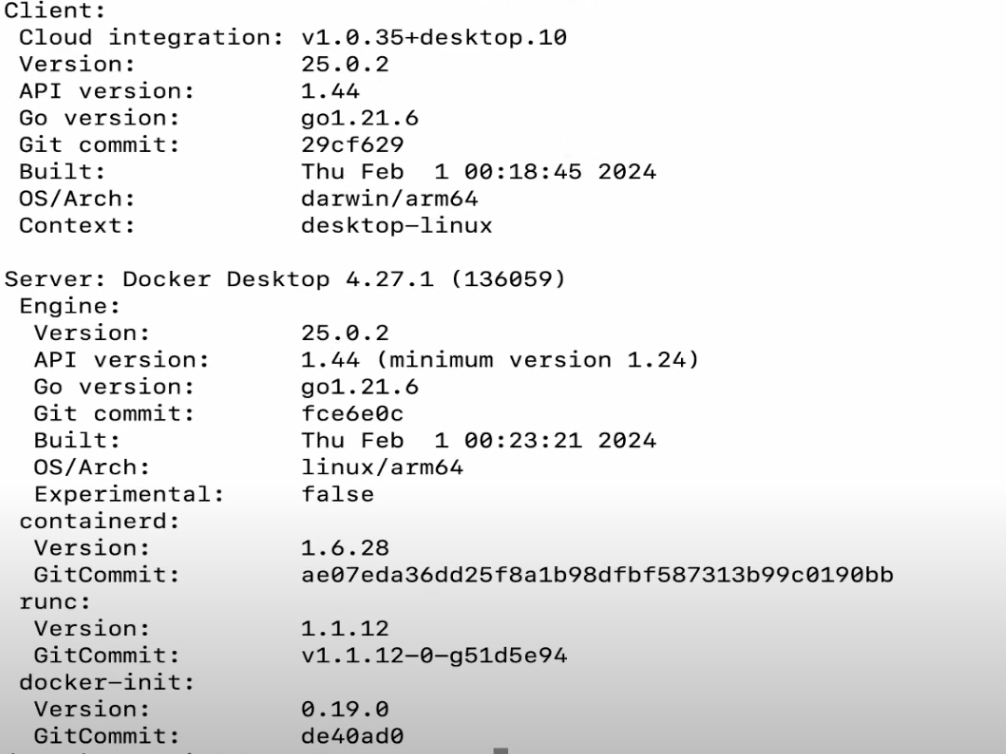
Open Terminal and run: docker --version. Expected output: Docker version 24.x.x
Run the hello-world test container: docker run hello-world. If successful, Docker will display a welcome message: Hello from Docker!

Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve successfully installed Docker on your computer, and your system is now ready to run containers and manage applications in an isolated environment. This is just the first step, but from here you can start experimenting with images, containers, and even creating your own Dockerized applications.
Related courses
See All CoursesIntermediate
Git Essentials
Git is the most popular version control system used by millions of developers around the globe. Whether you're a seasoned developer or a beginner, this course will equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to efficiently manage your software projects, collaborate with others, and master the art of version control.
Beginner
Linux Basics
Learning Linux is valuable for many IT professions. For system administrators, DevOps engineers, and backend developers, it enables efficient server management, automation of software development and deployment, and the development and management of server-side applications. For network administrators, cybersecurity professionals, and data analysts, Linux knowledge helps effectively manage networks, ensure security, and analyze data.
Content of this article