Related courses
See All CoursesIntermediate
In-Depth Python OOP
This course covers Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Python, starting with the basics and progressing to advanced concepts. You will implement a User model to gain practical experience and understanding of OOP features. By the end of the course, you will have a strong foundation in OOP and a deeper knowledge of Python's inner workings.
Beginner
Introduction to Python
Python is a high-level, interpreted, general-purpose programming language. Distinguished from languages such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, which are mainly utilized in web development, Python boasts versatility across multiple domains, including software development, data science, and back-end development. This course will guide you through Python's fundamental concepts, equipping you with the skills to create your own functions by the conclusion of the program.
Working with Environment Variables in Python
Harnessing the Power of Environment Variables for Secure and Flexible Coding

In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, the security and flexibility of applications are paramount. Python developers, aiming to craft robust and adaptable software, often turn to environment variables as a cornerstone of their development strategy. These variables serve as external configurations that can dictate how an application behaves in different environments without changing the codebase. This article delves into the utilization of environment variables in Python, providing insights into accessing, setting, and effectively managing them for enhanced security and configurability of applications.
Understanding Environment Variables
At their core, environment variables are key-value pairs that exist outside your application's source code. They are used to pass configuration data and sensitive information to your application at runtime. This approach is instrumental in keeping configurations dynamic and secure, allowing for the same application code to be used in different scenarios, such as development, testing, and production, without modifications.
Why Use Environment Variables?
The rationale behind using environment variables is threefold:
-
Security: By storing sensitive information like API keys, database passwords, and secret tokens in environment variables, they are kept out of the source code. This practice significantly mitigates the risk of sensitive data exposure, especially in open-source projects where the codebase is publicly accessible.
-
Flexibility and Scalability: Environment variables allow developers to change the application's behavior under different conditions without altering the code. This capability is crucial for deploying applications across various platforms and environments efficiently.
-
Portability: With environment variables, applications can be easily moved from one environment to another (e.g., from a developer's local machine to a production server) without the need for code changes. This makes the deployment process smoother and reduces the chances of errors.
Run Code from Your Browser - No Installation Required

Accessing Environment Variables in Python
Python's standard library includes the os module, which provides a convenient way of interacting with the operating system, including accessing environment variables. The os.getenv method is commonly used to retrieve the value of an environment variable, with the option to specify a default value if the variable is not found.
import os
# Accessing an environment variable
db_password = os.getenv('DB_PASSWORD')
# Checking if an environment variable exists
if db_password:
print("Database password found")
else:
print("Database password not found")
This simple mechanism ensures that your application can dynamically read its configuration, adapting to its current environment without manual intervention.
Setting Default Values
Specifying default values when accessing environment variables is a best practice, ensuring that your application has a fallback option if certain configurations are missing:
# Setting a default value if the environment variable is not found
db_host = os.getenv('DB_HOST', 'localhost')
This approach is particularly useful during development, where not all environment variables might be set up initially.
Setting Environment Variables in Python
While it's standard practice to set environment variables in the environment where the Python application is running, there are scenarios where you might want to set them directly within your code, especially for testing purposes:
os.environ['DEVELOPMENT_MODE'] = 'True'
However, this method should be used sparingly and with caution, as it can lead to differences between your development and production environments.
Start Learning Coding today and boost your Career Potential

Managing Environment Variables for Different Environments
To effectively manage environment variables across different environments (development, staging, production), developers often rely on .env files. These files contain environment-specific configurations, which can be loaded into the application at runtime. The python-dotenv package is a popular choice for this purpose, offering an easy way to load these variables:
- Installation: First, you need to install the
python-dotenvpackage using pip. - Creating and Loading
.envFiles: Create a.envfile at the root of your project and usepython-dotenvto load it into your application.
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv() # This loads the variables from '.env' into the environment
api_key = os.getenv('API_KEY')
This setup enables a smooth transition between different stages of development without the need to change the code.
Best Practices for Using Environment Variables
Adhering to best practices when using environment variables can greatly enhance the security and maintainability of your projects:
- Keep
.envfiles out of version control: To prevent accidental exposure of sensitive information,.envfiles should never be committed to version control repositories. Use.gitignoreto exclude them. - Use descriptive and consistent names: Choose clear and descriptive names for your environment variables to ensure that their purpose is immediately evident to anyone reviewing the code.
- Centralize access: Rather than scattering calls to
os.getenvthroughout your codebase, consider accessing environment variables in a single configuration module. This centralizes the configuration logic, making it easier to manage and update.
FAQs
Q: Do I need to install any additional packages to use environment variables in Python?
A: Basic access to environment variables does not require additional packages, as it's supported by the built-in os module. However, for more advanced management, such as loading variables from .env files, the python-dotenv package is recommended.
Q: How do I keep my environment variables secure?
A: Always store sensitive information in environment variables instead of hardcoding them in your application. Use .env files for local development and secure storage solutions like secret managers in cloud environments for production.
Q: Can environment variables be used for configuration files?
A: Yes, environment variables are perfect for storing configuration settings that vary between environments. This allows you to maintain a single codebase that can be deployed in multiple settings.
Q: Is it possible to set environment variables temporarily?
A: Yes, you can set environment variables temporarily within your development environment or programmatically within your Python code. However, remember that changes made programmatically with os.environ are only effective for the current process and its children.
Q: How do environment variables work with virtual environments in Python?
A: Environment variables are system-level settings, meaning they are accessible regardless of the Python virtual environment in use. However, tools like python-dotenv can help you manage different sets of variables for each project or environment, aligning with the isolation provided by virtual environments.
Related courses
See All CoursesIntermediate
In-Depth Python OOP
This course covers Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Python, starting with the basics and progressing to advanced concepts. You will implement a User model to gain practical experience and understanding of OOP features. By the end of the course, you will have a strong foundation in OOP and a deeper knowledge of Python's inner workings.
Beginner
Introduction to Python
Python is a high-level, interpreted, general-purpose programming language. Distinguished from languages such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, which are mainly utilized in web development, Python boasts versatility across multiple domains, including software development, data science, and back-end development. This course will guide you through Python's fundamental concepts, equipping you with the skills to create your own functions by the conclusion of the program.
The SOLID Principles in Software Development
The SOLID Principles Overview
by Anastasiia Tsurkan
Backend Developer
Nov, 2023・8 min read

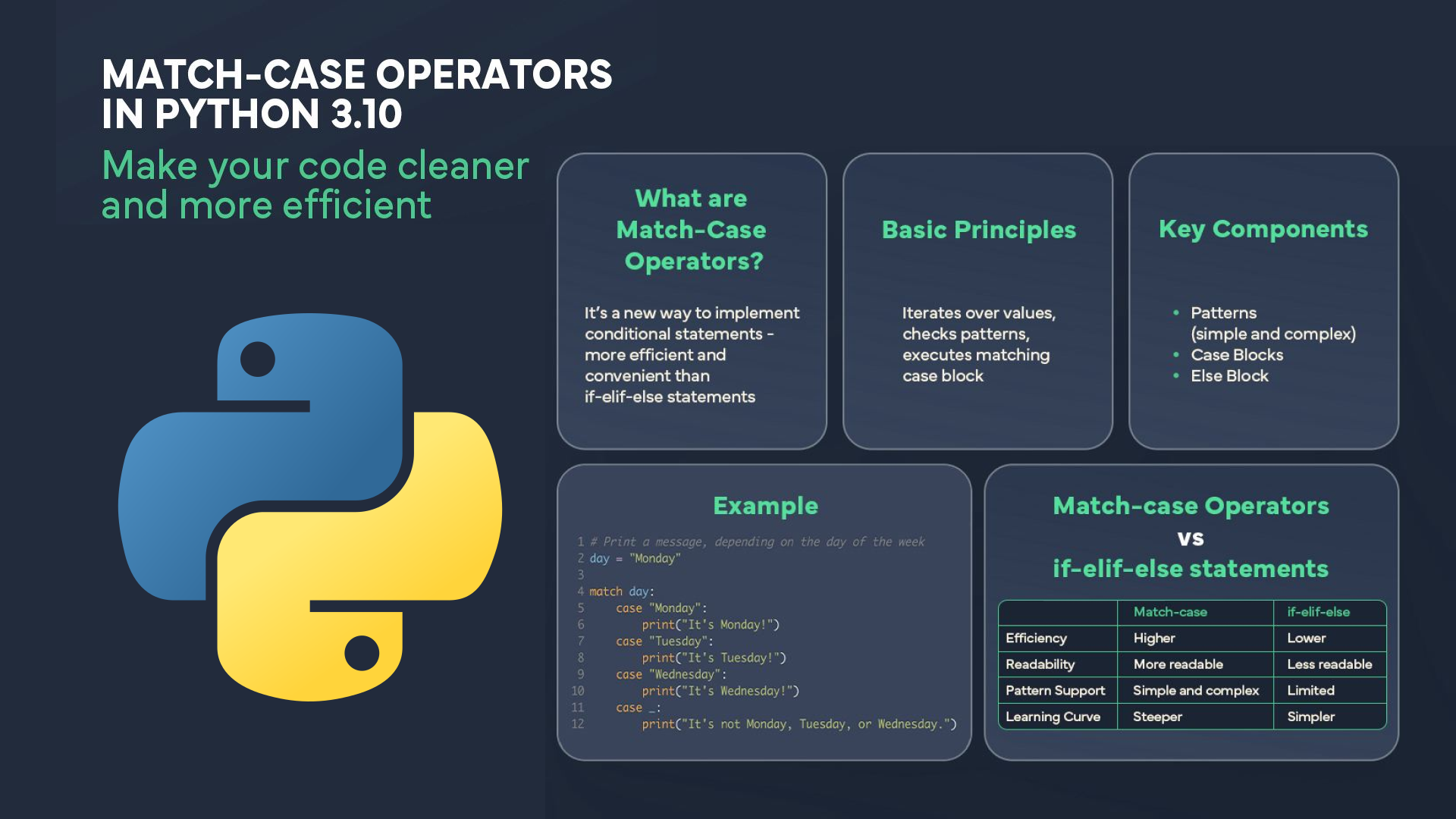
Match-case Operators in Python
Match-case Operators vs if-elif-else statements
by Oleh Lohvyn
Backend Developer
Dec, 2023・6 min read
30 Python Project Ideas for Beginners
Python Project Ideas
by Anastasiia Tsurkan
Backend Developer
Sep, 2024・14 min read

Content of this article