Gerelateerde cursussen
Bekijk Alle CursussenBeginner
Explainable AI (XAI) Basics
Gain a foundational understanding of Explainable AI (XAI): what it is, why it matters, key concepts, main techniques, and ethical considerations. This course is theory-focused, using clear explanations and quizzes to build your intuition about making AI systems more transparent and trustworthy.
Halfgevorderd
Generative Adversarial Networks Basics
A comprehensive, theory-focused introduction to Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), covering their intuition, mathematical foundations, training dynamics, key variants, and real-world challenges. This course is designed for learners seeking a deep conceptual understanding of GANs without coding.
Automating AI Evaluation with LLM-as-a-Judge
Replacing Manual Review with Scalable AI Grading

You have built a RAG application. It answers questions based on your documents. But how do you know if it is actually good?
In traditional software, you write unit tests:
It's simple. In Generative AI, the answer to "Summarize this article" changes every time. You cannot write a simple assertion.
Most developers rely on the "Vibe Check" — they manually read 10 answers and decide if they "feel" right. This is not engineering. This is guessing. To build reliable AI systems, you need a reliable way to measure quality. You need LLM-as-a-Judge.
The Concept of AI Grading AI
The core idea is simple. You use a highly capable model (like GPT-4o) to evaluate the outputs of your application (which might use a faster, cheaper model like Llama-3 or GPT-3.5).
The "Judge" model is given a strict rubric, just like a teacher grading an essay.
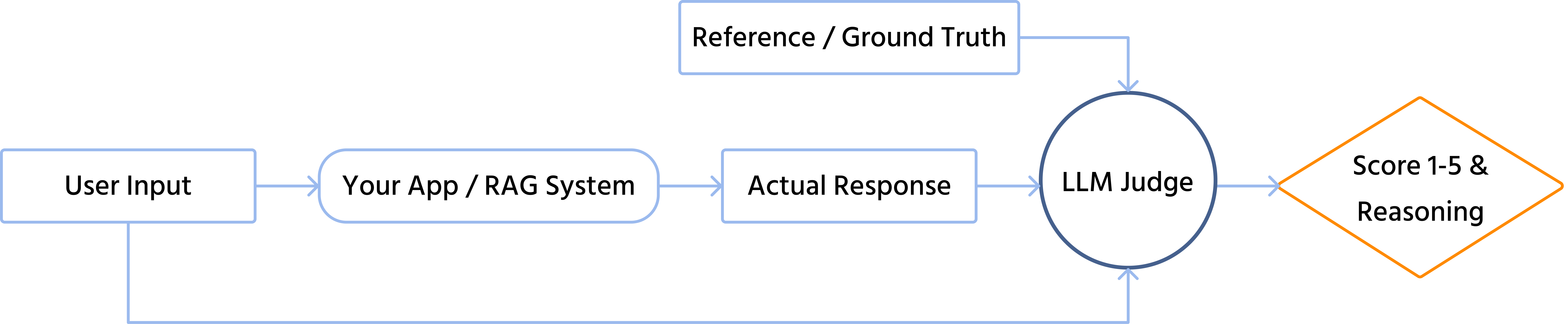
How to Implement a Judge
To implement this, you need a prompt that instructs the Judge on how to score. Here is a simplified example of a Python function that evaluates "Relevance".
Comparison of Human Eval vs LLM Eval
| Feature | Human Evaluation | LLM-as-a-Judge |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slow (Minutes per item) | Fast (Seconds per item) |
| Cost | High (Hourly wages) | Medium (API costs) |
| Scalability | Low (Cannot grade 10k rows daily) | High (Can grade millions) |
| Consistency | Varies (Mood/fatigue affects score) | Stable (Deterministic with temp=0) |
| Nuance | High (Understands subtle context) | Medium (Can miss subtle sarcasm) |
Practical Use Cases
Implementing LLM-as-a-Judge allows you to treat AI development like standard software engineering.
CI/CD for Prompts
Imagine you want to change your system prompt to make the bot more polite. Before pushing to production, you run a test suite of 100 questions. The Judge evaluates both the old and new answers. If the "Accuracy" score drops, the pipeline fails, and you know you broke something.
RAG Retrieval Scoring
You can use a Judge to evaluate the intermediate steps of your RAG pipeline.
- Context Relevance: did the database return useful documents?
- Faithfulness: did the bot answer based only on those documents, or did it hallucinate?
Trade-offs
This approach is not perfect. Self-Bias is a known issue where a model might prefer answers generated by itself or models from the same family. Also, if the Judge is not smarter than the model being evaluated, the scores may be inaccurate.
Gerelateerde cursussen
Bekijk Alle CursussenBeginner
Explainable AI (XAI) Basics
Gain a foundational understanding of Explainable AI (XAI): what it is, why it matters, key concepts, main techniques, and ethical considerations. This course is theory-focused, using clear explanations and quizzes to build your intuition about making AI systems more transparent and trustworthy.
Halfgevorderd
Generative Adversarial Networks Basics
A comprehensive, theory-focused introduction to Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), covering their intuition, mathematical foundations, training dynamics, key variants, and real-world challenges. This course is designed for learners seeking a deep conceptual understanding of GANs without coding.
The Architecture Of Liquid Neural Networks
How Brain Inspired AI Adapts In Real Time After Training
by Arsenii Drobotenko
Data Scientist, Ml Engineer
Mar, 2026・6 min read

Moving Beyond Text with World Models and Physical Reality
Why the Next Frontier of Intelligence Is Not Written in Tokens
by Arsenii Drobotenko
Data Scientist, Ml Engineer
Feb, 2026・6 min read
Proving Bigger Isn't Always Better Using Small Language Models
How Compact Models Are Revolutionizing Privacy, Cost, and Edge Computing
by Arsenii Drobotenko
Data Scientist, Ml Engineer
Feb, 2026・7 min read

Inhoud van dit artikel