Cursos relacionados
Ver Todos os CursosIntermediário
Git Essentials
Git is the most popular version control system used by millions of developers around the globe. Whether you're a seasoned developer or a beginner, this course will equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to efficiently manage your software projects, collaborate with others, and master the art of version control.
Intermediário
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Discover the world of cloud computing by exploring its core technologies and practical applications in this course! Begin with the fundamentals of cloud computing and then focus on essential AWS services like S3 (Simple Storage Service) for scalable storage, EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) for virtual servers, and RDS (Relational Database Service) for managed databases. Gain hands-on experience as you learn how these services integrate to support modern applications efficiently.
Intermediário
AWS Solutions Architect Associate
This course is designed to help you master the skills required to become an AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate. You'll gain a deep understanding of AWS services, architecture best practices, and real-world cloud solutions. Through hands-on exercises and detailed explanations, you'll learn how to design scalable, cost-efficient, and secure applications on AWS.
Installing Jenkins with Docker
Easily deploy Jenkins with Docker for a fast and isolated CI/CD environment.

Jenkins is one of the most popular automation tools for building, testing, and deploying applications. It plays a key role in DevOps practices and CI/CD pipelines, helping teams release updates faster while maintaining code quality.
In this guide, we’ll walk through setting up Jenkins LTS (Long-Term Support) using Docker. Running Jenkins in Docker makes the setup process much simpler, as it provides an isolated environment without manual server configuration.
👉 If you don’t already have Docker installed, follow this official installation guide before continuing.
Run Jenkins in a Docker Container
First, pull the latest Jenkins LTS image from Docker Hub. Open your terminal and run:
docker pull jenkins/jenkins:lts
Now, start a Jenkins container:
docker run -d -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 --name jenkins-container -v jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home jenkins/jenkins:lts
What the flags mean:
-d— runs the container in detached mode (background).-p 8080:8080— maps Jenkins to port 8080 (web access);-p 50000:50000— port for connecting Jenkins agents;-v jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home— creates a persistent volume for Jenkins data, so your configuration won’t be lost when the container restarts.
Once the container is running, open:
http://localhost:8080
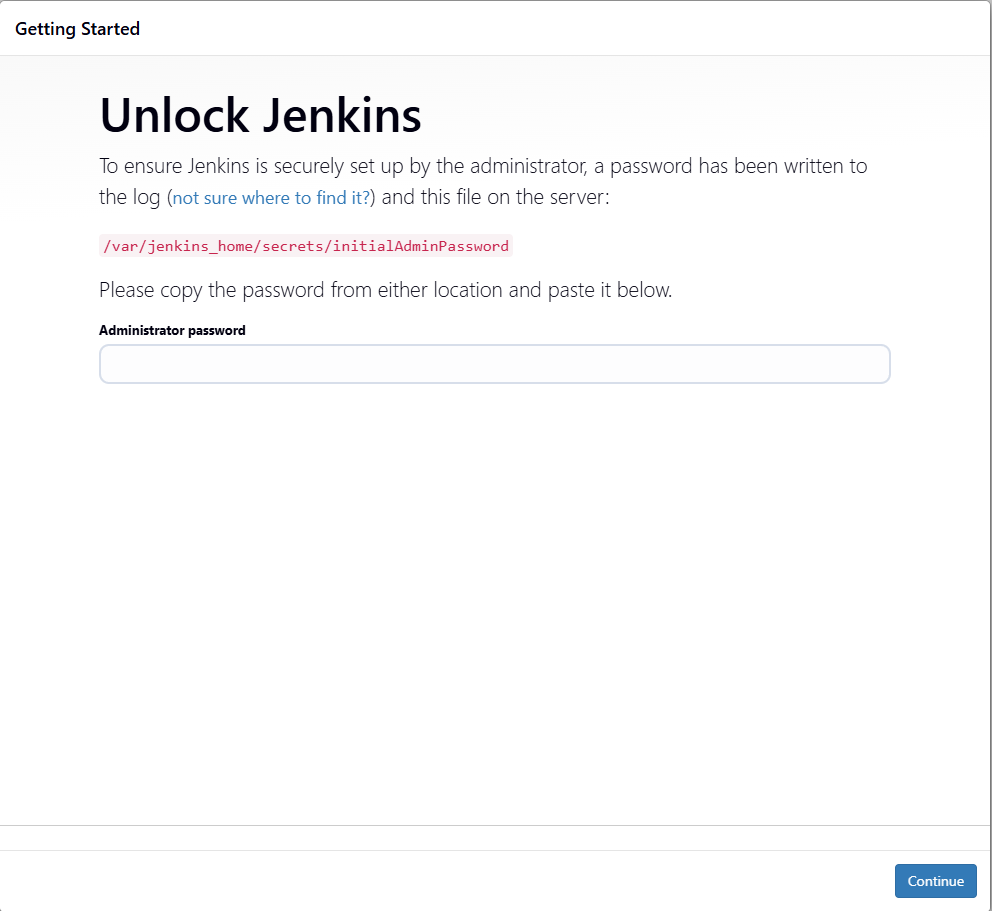
When Jenkins first starts, it requires an admin password. To retrieve it, run:
docker exec jenkins-container cat /var/jenkins_home/secrets/initialAdminPassword
Copy the password and paste it into the Jenkins setup screen.

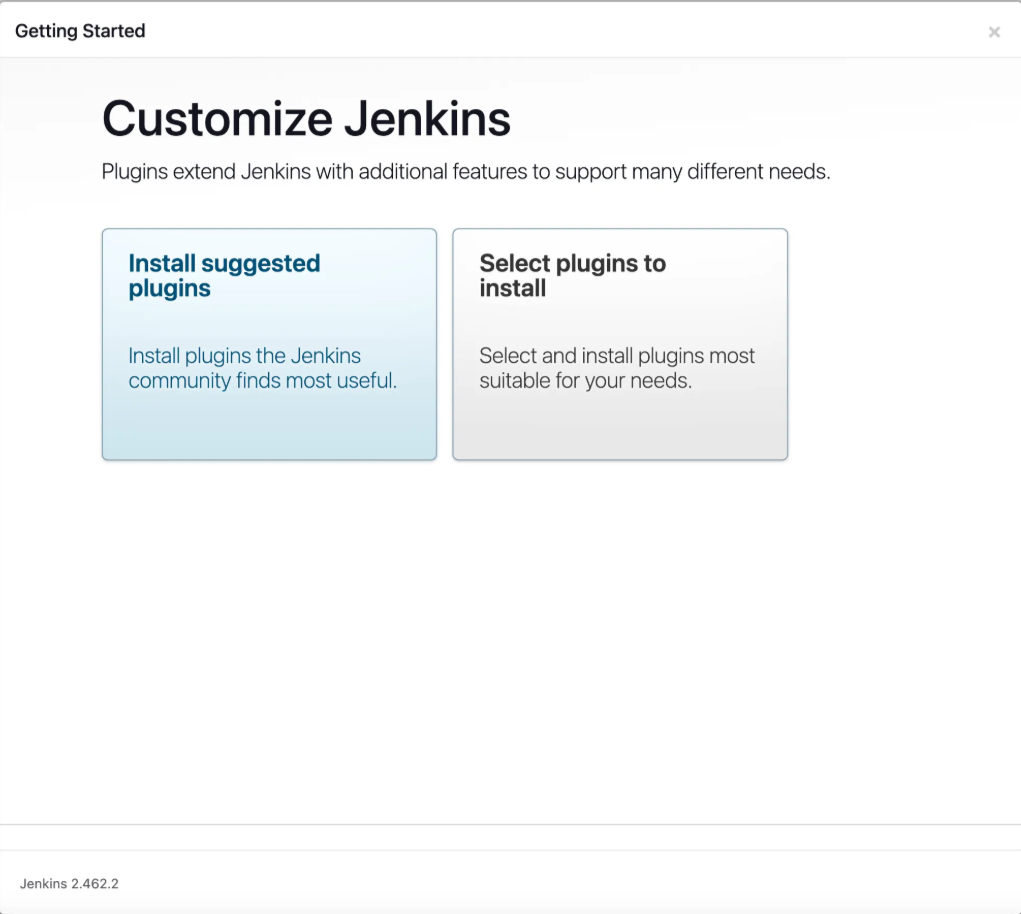
Jenkins will now prompt you to install plugins. Select Install Suggested Plugins to get the recommended set.
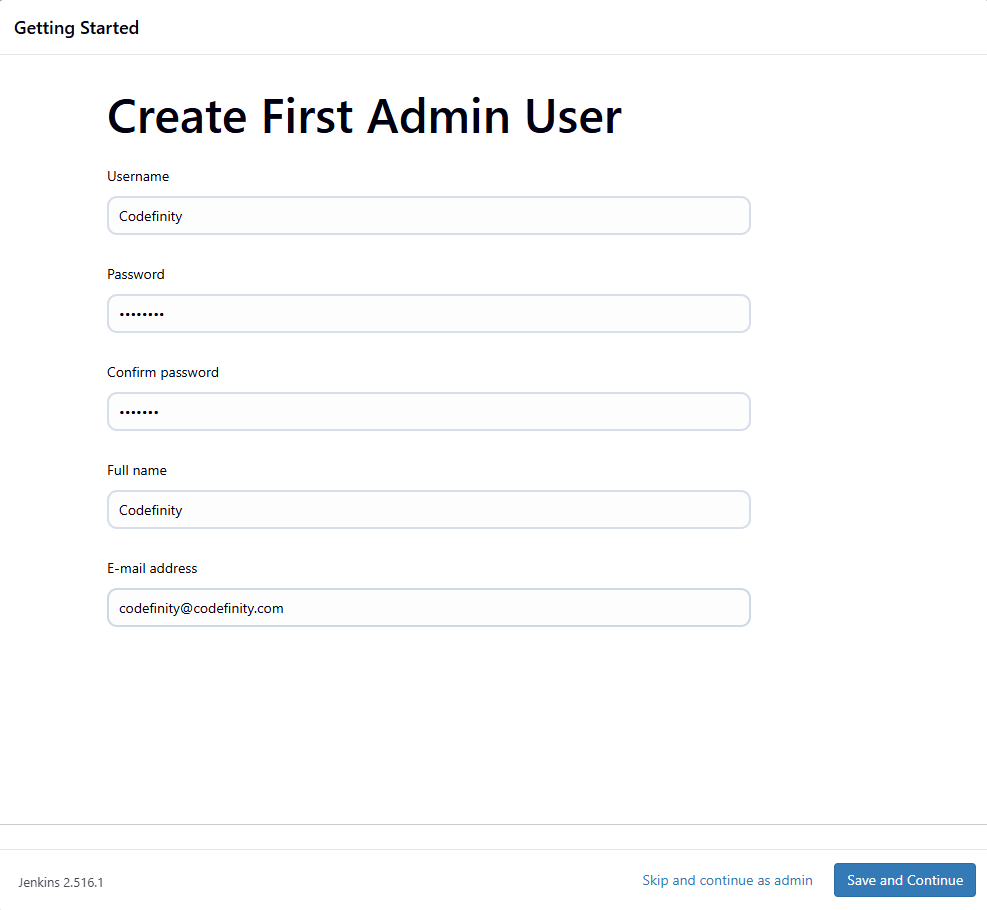
Next, set up your admin account by filling out the form with:
- Username;
- Password;
- Full name;
- Email.
Jenkins will suggest a default URL, usually http://localhost:8080/.
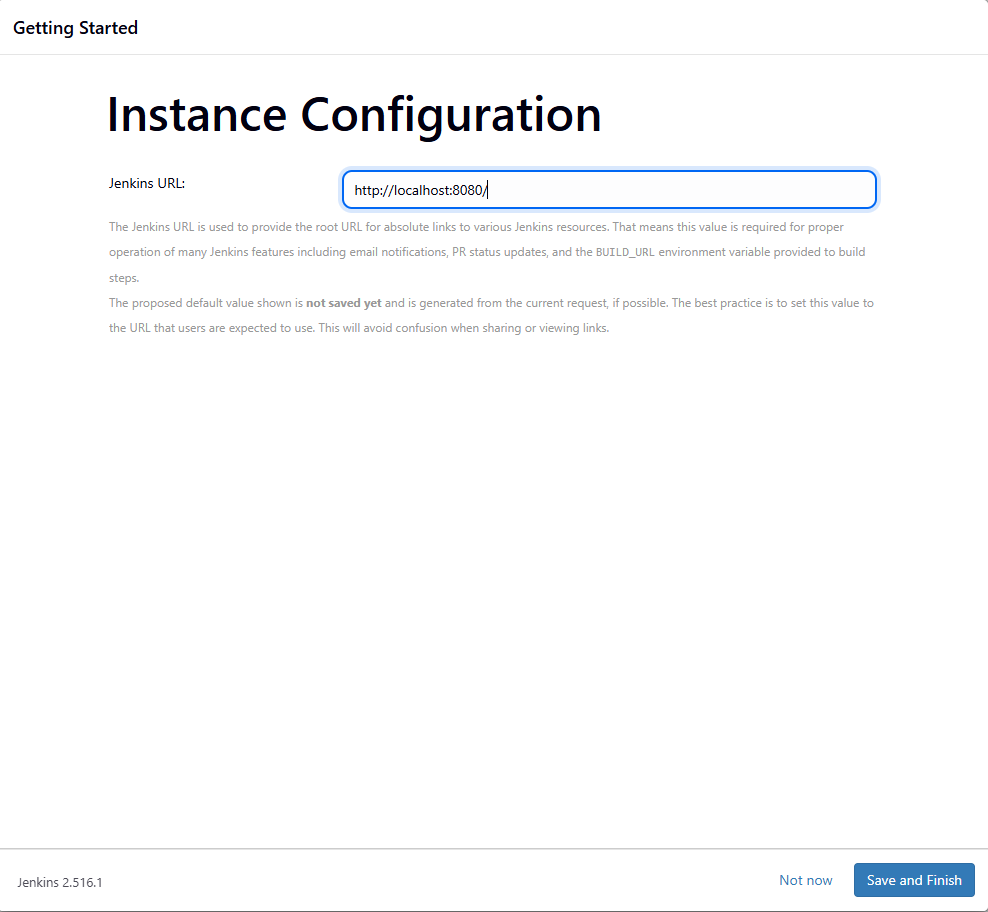
Leave it as is and click Save and Finish.
That’s it! Jenkins is now ready to use.
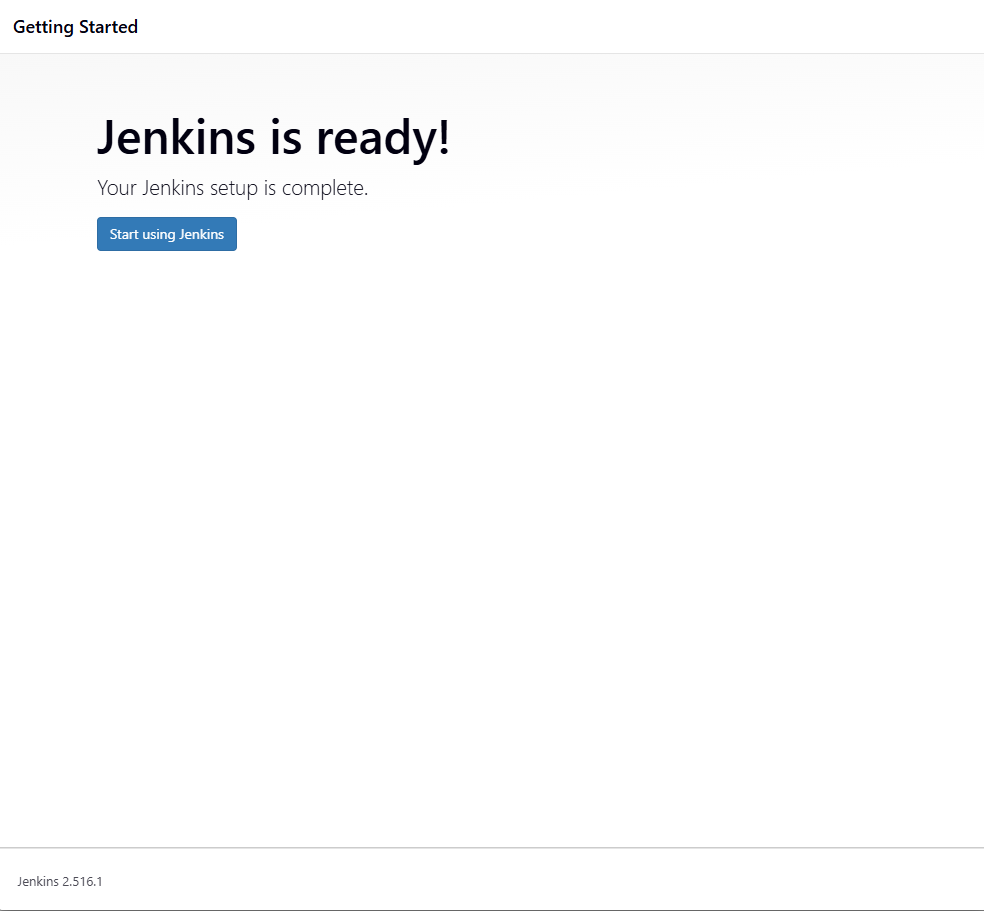
Conclusion
We successfully deployed Jenkins inside a Docker container. This setup provides several benefits:
- Fast and isolated CI/CD environment setup;
- Persistent data storage with Docker volumes;
- Easy updates and portability.
From here, you can start creating pipelines, adding agents, and integrating Jenkins with your version control system.
Start Learning Coding today and boost your Career Potential

Cursos relacionados
Ver Todos os CursosIntermediário
Git Essentials
Git is the most popular version control system used by millions of developers around the globe. Whether you're a seasoned developer or a beginner, this course will equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to efficiently manage your software projects, collaborate with others, and master the art of version control.
Intermediário
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Discover the world of cloud computing by exploring its core technologies and practical applications in this course! Begin with the fundamentals of cloud computing and then focus on essential AWS services like S3 (Simple Storage Service) for scalable storage, EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) for virtual servers, and RDS (Relational Database Service) for managed databases. Gain hands-on experience as you learn how these services integrate to support modern applications efficiently.
Intermediário
AWS Solutions Architect Associate
This course is designed to help you master the skills required to become an AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate. You'll gain a deep understanding of AWS services, architecture best practices, and real-world cloud solutions. Through hands-on exercises and detailed explanations, you'll learn how to design scalable, cost-efficient, and secure applications on AWS.
Exploring ARM and AMD x86 Processor Designs
Battle of Architectures
by Oleh Lohvyn
Backend Developer
Apr, 2024・5 min read

Python Projects for Beginners
Python Projects
by Andrii Chornyi
Data Scientist, ML Engineer
Dec, 2023・8 min read
Guide to Installing Kubernetes on Windows and Mac
A beginner-friendly guide to getting Kubernetes up and running on your computer.
by Eugene Obiedkov
Full Stack Developer
Aug, 2025・6 min read
Conteúdo deste artigo