Cursos relacionados
Ver Todos os CursosAvançado
Transformers Theory Essentials
A comprehensive, code-free exploration of transformer-based language models, focusing on their architecture, text generation mechanics, and the theoretical principles underlying their behavior.
Avançado
Mathematical Foundations of Neural Networks
Gain a rigorous mathematical understanding of neural networks as function approximators. Explore their linear-algebraic structure, approximation power, and the fundamental role of depth in expressivity—without implementation or training details.
Moving Beyond Text with World Models and Physical Reality
Why the Next Frontier of Intelligence Is Not Written in Tokens
For the past few years, the artificial intelligence landscape has been dominated by a single paradigm: the Large Language Model (LLM). You have likely seen these models ingest nearly every piece of text ever published to the internet, creating systems with uncanny abilities to summarize, translate, and generate human-like prose.
But as impressive as systems like GPT-4 and Claude 3 are, they are beginning to hit a fundamental ceiling. Language is just a lossy compression map of reality. It is not reality itself. An AI trained solely on text knows everything about the world, but it understands very little of it.
You are now entering a new phase of AI research and engineering. The focus is shifting away from simply scaling transformer models with more text data and toward developing World Models. This represents a transition from an AI that can describe gravity to an AI that intuitively understands that if it drops a glass, it will fall and shatter.
The Limits of the Token Prison
LLMs exist in what researchers call a "Token Prison". Their entire universe consists of discrete sequences of text tokens. They lack sensory grounding in the physical world.
Consider a classic scenario. You can ask an LLM to provide a detailed, step-by-step guide on how to ride a bicycle. It will generate a perfect response, explaining balance, pedaling, and braking. Yet, if you were to download that exact model's weights into a humanoid robot and place it on a bicycle, it would immediately crash.
Why? Because the LLM has no concept of balance as a physical sensation. It doesn't understand momentum, friction, or gravity as forces that act upon a body. It only understands the linguistic relationships between the words describing those concepts. It is predicting sequences, not consequences.
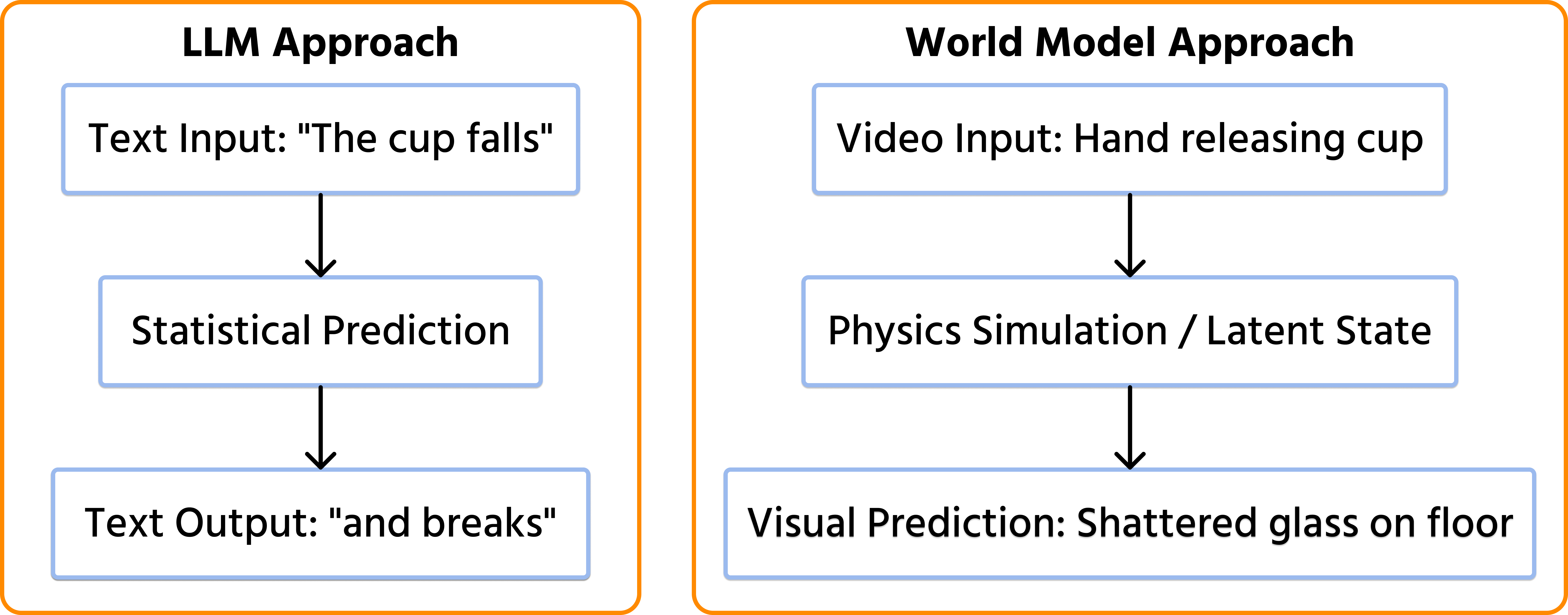
Visualizing the Difference
To understand why this matters, look at how an LLM processes a falling object versus how a World Model processes it.
Run Code from Your Browser - No Installation Required

Deconstructing the World Model Architecture
A World Model is fundamentally different from an LLM. While an LLM's goal is to predict the next token given a sequence of previous tokens, a World Model's goal is to build an internal simulation of the environment to predict future states.
This approach generally consists of three key components that mimic biological cognition:
- Perception (the encoder): instead of ingesting static text, a World Model consumes high-bandwidth, multimodal sensor data – video streams, LiDAR point clouds, and joint torque sensors. It compresses this noisy data into a compact "latent state";
- The transition function (the physics engine): this is the core brain. It learns a transition function that predicts how the world changes. Given the current state and a proposed action, the model predicts the next likely state;
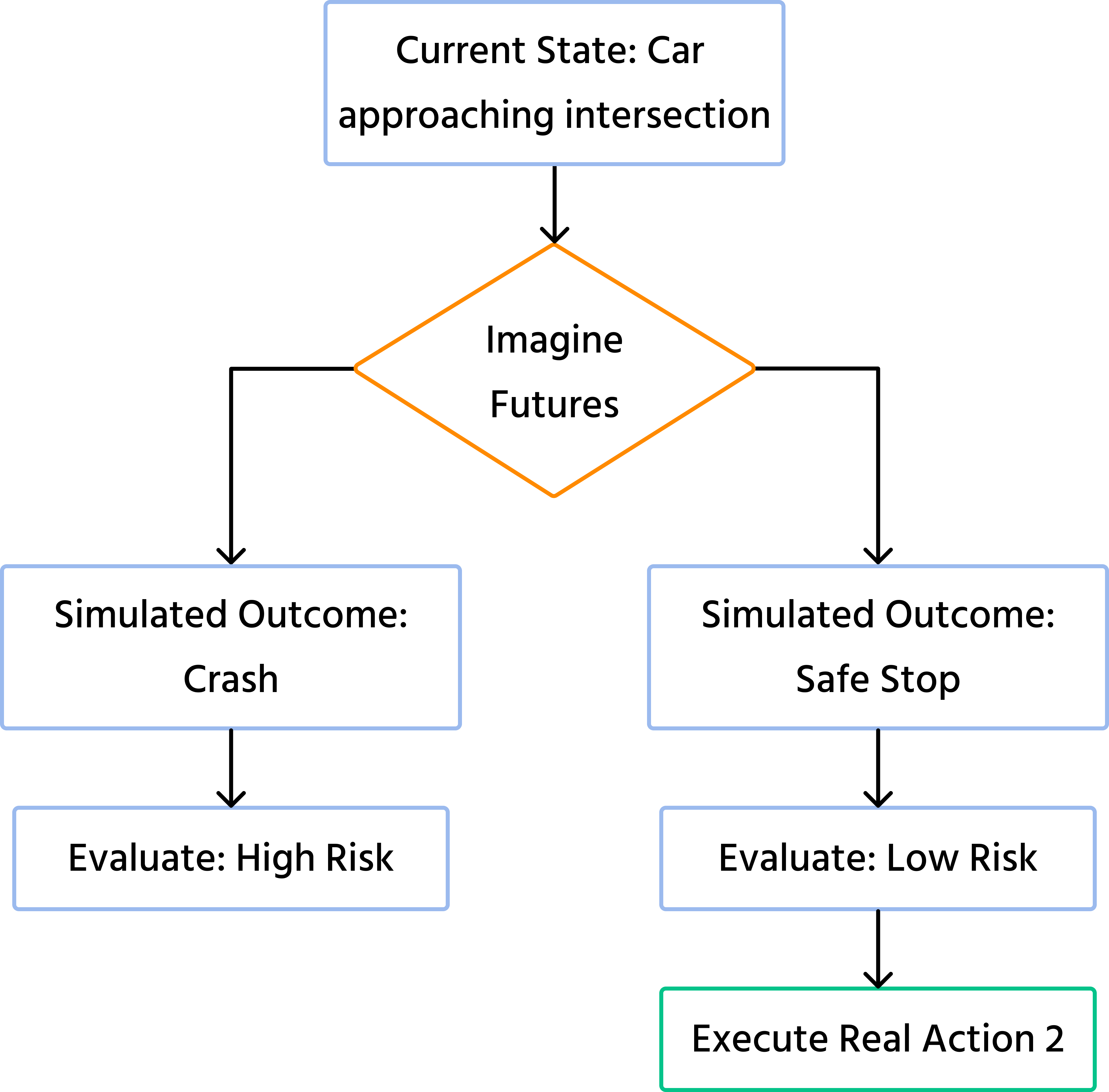
- Imagination (the planner): because the model can predict future states, it can dream. Before taking a real-world action, the agent can run thousands of simulations in its internal world model to see what would happen.
The Imagination Loop
This "dreaming" capability allows the AI to plan safety without risking damage in the real world.
The Shift to Embodied AI
The true potential of World Models is realized in Embodied AI – giving neural networks a physical form, whether it's a robotic arm in a factory, a drone inspecting infrastructure, or a humanoid robot in a home.
For decades, robotics suffered from Moravec's Paradox. High-level reasoning (like playing chess) requires very little computation, but low-level sensorimotor skills (like a one-year-old child walking across a room) require enormous computational resources. LLMs solved the chess problem. World Models are solving the walking problem.
When a model understands the physics of its environment, it becomes robust to novelty. An old-school industrial robot needs to be programmed with exact coordinates to pick up a specific part. A robot powered by a World Model can look at a bin full of jumbled, unfamiliar parts, simulate the physics of grasping them, and successfully pick one up on the first try without explicit training for that specific object.
Comparing Paradigms Text vs Reality
| Feature | Large Language Models (LLMs) | World Models |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Input Data | Static text datasets (internet crawls) | High-frequency sensor data (video, depth, touch) |
| Core Objective | Predict the next text token based on stats | Predict the next state based on causality |
| Understanding of Physics | Semantic (knows the word "gravity") | Functional (understands how gravity acts) |
| Reasoning Capability | Chain-of-thought based on patterns | Spatial simulation and planning |
| Primary Applications | Content generation, coding, chatbots | Autonomous driving, robotics, spatial computing |
Start Learning Coding today and boost your Career Potential

Conclusion
You are standing on the precipice of a major divergence in AI engineering. While LLMs will continue to evolve as linguistic interfaces, the engines of physical action will be built on World Models.
The next "GPT moment" will not be a chatbot that writes slightly better poetry. It will be a system that watches a video of a complex machine breaking down, understands the physical chain of events that caused the failure, and can physically manipulate tools to fix it. By moving beyond text, AI moves from simply knowing things to truly understanding how the world works.
Cursos relacionados
Ver Todos os CursosAvançado
Transformers Theory Essentials
A comprehensive, code-free exploration of transformer-based language models, focusing on their architecture, text generation mechanics, and the theoretical principles underlying their behavior.
Avançado
Mathematical Foundations of Neural Networks
Gain a rigorous mathematical understanding of neural networks as function approximators. Explore their linear-algebraic structure, approximation power, and the fundamental role of depth in expressivity—without implementation or training details.
Automating AI Evaluation with LLM-as-a-Judge
Replacing Manual Review with Scalable AI Grading
by Arsenii Drobotenko
Data Scientist, Ml Engineer
Feb, 2026・5 min read

Synthetic Data and the Future of AI Training
How to Train Models When Real Data Is Scarce or Sensitive
by Arsenii Drobotenko
Data Scientist, Ml Engineer
Feb, 2026・5 min read

Proving Bigger Isn't Always Better Using Small Language Models
How Compact Models Are Revolutionizing Privacy, Cost, and Edge Computing
by Arsenii Drobotenko
Data Scientist, Ml Engineer
Feb, 2026・7 min read

Conteúdo deste artigo