Related courses
See All CoursesBeginner
Introduction to JavaScript
Learn the fundamentals of JavaScript, the backbone of dynamic web development. Discover essential concepts like syntax, variables, data types, and operators. Explore how to use conditional statements, loops, and functions to create interactive and efficient programs. Master the building blocks of JavaScript and lay the groundwork for more advanced programming skills.
Beginner
Introduction to TypeScript
This course is designed for absolute beginners who want to master the basics of the TypeScript programming language. TypeScript is a modern and powerful language that extends the capabilities of JavaScript, making your code more reliable and readable. We will start from the very basics, covering variables, data types, comparison operators, and conditional statements. Then, we will delve into working with arrays and loops. Upon completing this course, you will be ready to create simple programs in TypeScript and continue your learning journey into more advanced topics.
Mastering TypeScript Generics
TypeScript Generics

Introduction
In the rapidly changing landscape of software development, the search for code that is both sturdy and adaptable remains crucial. TypeScript generics are an effective feature that empowers developers to write code that is more flexible and widely applicable, especially in libraries and frameworks.
In this article, we will explore the realm of generics in TypeScript, discussing their intricacies, advantages, and best practices to fully utilize their potential in creating resilient and scalable software solutions.
Understanding Generics
Generics in TypeScript provide a mechanism for writing code that can work with a variety of data types while maintaining type safety. At their core, generics allow developers to define functions, classes, and interfaces in a way that abstracts over the specific types they operate on, enabling the creation of reusable components that are agnostic to the exact data they manipulate.
Run Code from Your Browser - No Installation Required

Benefits of Generics
The utilization of generics bestows several advantages upon software development endeavors:
- Flexibility: Generics enable the creation of versatile components that can seamlessly adapt to different data types, promoting code reuse across a wide range of scenarios.
- Type Safety: TypeScript's type inference capabilities extend to generics, ensuring that type errors are caught at compile time rather than runtime, thereby enhancing code reliability and maintainability.
- Abstraction: Generics facilitate the abstraction of common patterns and behaviors, allowing developers to build higher-level abstractions that encapsulate complex functionality without sacrificing clarity or type correctness.
Exploring Generics in Practice
Let's delve into practical examples to elucidate the utilization of generics in TypeScript:
Example 1: Generic Functions
Consider a scenario where we want to implement a function to merge two arrays of the same type:
function mergeArrays<T>(arr1: T[], arr2: T[]): T[] {
return [...arr1, ...arr2];
}
const mergedArray = mergeArrays([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]);
console.log(mergedArray); // Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
const mergedStringArray = mergeArrays(["a", "b"], ["c", "d"]);
console.log(mergedStringArray); // Output: ["a", "b", "c", "d"]
In this example:
- The
mergeArraysfunction takes two arrays of typeTand returns a new array containing elements from both arrays. - The generic type parameter
Tallows the function to work with arrays of any type, providing flexibility and reusability.
Example 2: Generic Classes
Let's implement a generic Pair class to represent a pair of values:
class Pair<T, U> {
private first: T;
private second: U;
constructor(first: T, second: U) {
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
getFirst(): T {
return this.first;
}
getSecond(): U {
return this.second;
}
}
const numberStringPair = new Pair<number, string>(10, "hello");
console.log(numberStringPair.getFirst()); // Output: 10
console.log(numberStringPair.getSecond()); // Output: "hello"
Here:
- The
Pairclass is defined with two generic type parameters,TandU, representing the types of the first and second values, respectively. - The class constructor accepts values of types
TandU, allowing the creation of pairs with different types of elements. - The
getFirstandgetSecondmethods retrieve the first and second values of the pair, respectively.
Example 3: Type Constraints
Let's enhance the mergeArrays function to only accept arrays containing elements that can be concatenated:
function mergeArrays<T extends Array<any>>(arr1: T, arr2: T): T {
return [...arr1, ...arr2];
}
const mergedArray = mergeArrays([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]);
console.log(mergedArray); // Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
const invalidArray = mergeArrays([1, 2, 3], ["a", "b", "c"]); // Error: Argument of type 'string[]' is not assignable to parameter of type 'number[]'
Here:
- We've added a type constraint
<T extends Array<any>>to the generic type parameterT, specifying thatTmust be an array (Array<any>). - This constraint ensures that the
mergeArraysfunction can only be used with arrays, preventing errors when trying to merge non-array types. - Attempting to merge arrays of different element types results in a compile-time error, enforcing type safety.
Example 4: Generic Interface
Let's define a generic interface for a key-value pair:
interface KeyValuePair<K, V> {
key: K;
value: V;
}
const pair: KeyValuePair<number, string> = { key: 1, value: "hello" };
console.log(pair.key); // Output: 1
console.log(pair.value); // Output: "hello"
Here:
- The
KeyValuePairinterface defines two generic type parameters,Kfor the key type andVfor the value type. - We declare a variable
pairof typeKeyValuePair<number, string>where the key is a number and the value is a string.
Conclusion
Generics in TypeScript offer a powerful mechanism for writing flexible and reusable code, particularly within libraries and frameworks. By abstracting over specific data types, generics enable the creation of components that are adaptable to diverse scenarios while upholding type safety and code clarity.
Start Learning Coding today and boost your Career Potential

FAQs
Q: What are TypeScript generics?
A: TypeScript generics are a feature that helps write flexible code that can work with different data types while maintaining type safety.
Q: Why are generics important in TypeScript?
A: Generics are important because they allow developers to create reusable components that can adapt to different data types, making code more versatile and reliable.
Q: How do generics benefit software development?
A: Generics make code more flexible, type-safe, and reusable, which simplifies development and reduces the likelihood of errors.
Q: Can you give an example of generics in TypeScript?
A: Sure! For instance, you can use generics to create a function that merges arrays of any type, making it adaptable to various scenarios.
Q: What is the main advantage of using generics in TypeScript?
A: The main advantage is that generics allow developers to write code that is both adaptable to different data types and type-safe, ensuring fewer errors at runtime.
Related courses
See All CoursesBeginner
Introduction to JavaScript
Learn the fundamentals of JavaScript, the backbone of dynamic web development. Discover essential concepts like syntax, variables, data types, and operators. Explore how to use conditional statements, loops, and functions to create interactive and efficient programs. Master the building blocks of JavaScript and lay the groundwork for more advanced programming skills.
Beginner
Introduction to TypeScript
This course is designed for absolute beginners who want to master the basics of the TypeScript programming language. TypeScript is a modern and powerful language that extends the capabilities of JavaScript, making your code more reliable and readable. We will start from the very basics, covering variables, data types, comparison operators, and conditional statements. Then, we will delve into working with arrays and loops. Upon completing this course, you will be ready to create simple programs in TypeScript and continue your learning journey into more advanced topics.
The SOLID Principles in Software Development
The SOLID Principles Overview
by Anastasiia Tsurkan
Backend Developer
Nov, 2023・8 min read

30 Python Project Ideas for Beginners
Python Project Ideas
by Anastasiia Tsurkan
Backend Developer
Sep, 2024・14 min read

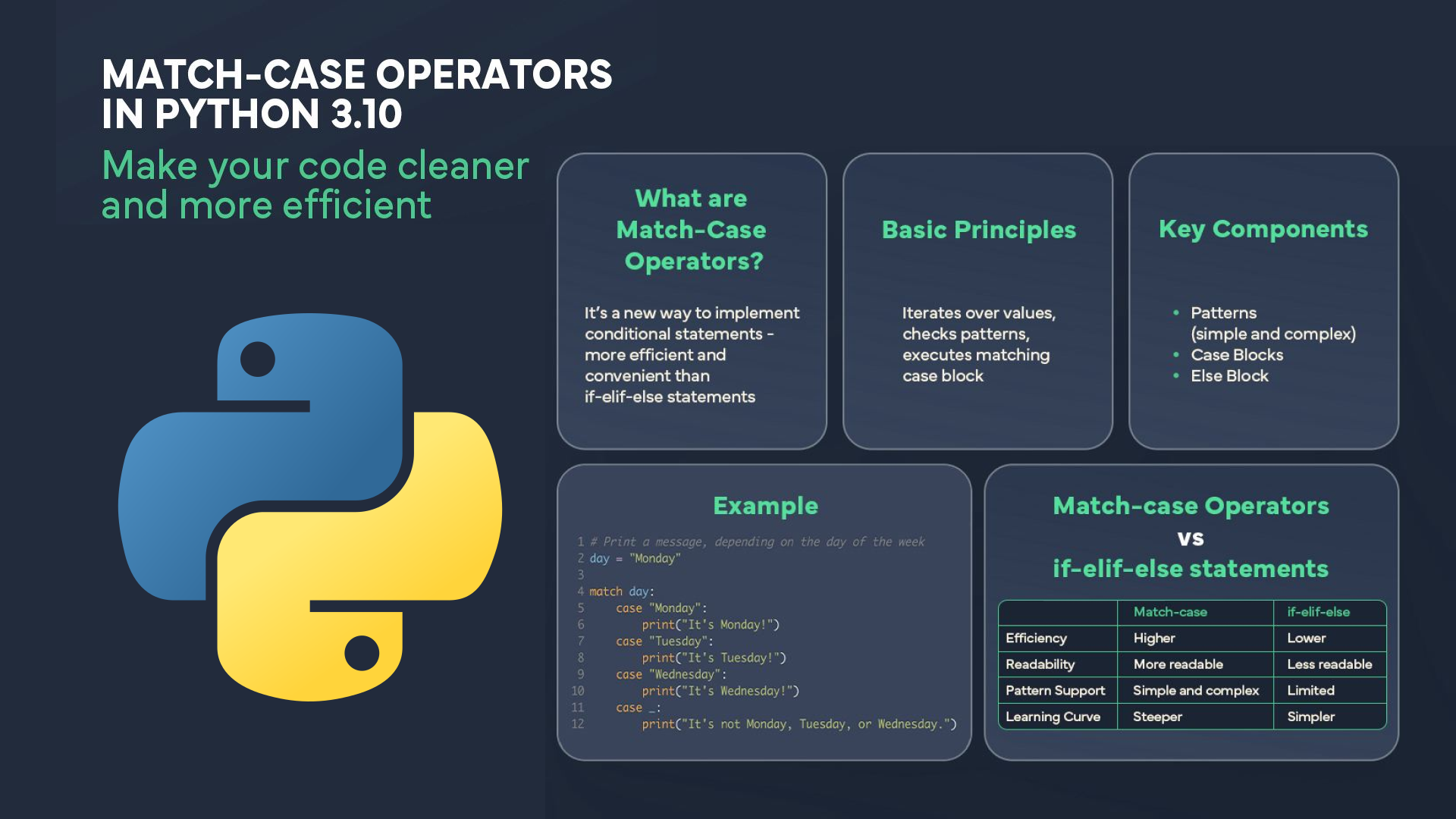
Match-case Operators in Python
Match-case Operators vs if-elif-else statements
by Oleh Lohvyn
Backend Developer
Dec, 2023・6 min read
Content of this article